Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), is a serious medical condition that can be deadly if left untreated. It can occur when the blood vessels in your kidneys become damaged and inflamed, causing clots to form in the vessels. These clots have the ability clog the filtering system in your kidneys, and lead to kidney failure.
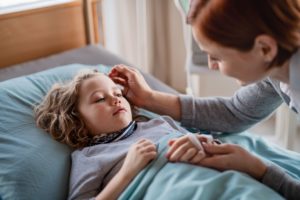
Often, HUS is caused by infections that are triggered by certain strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria. Though anyone can develop HUS, it most commonly affects young children.
In addition to infections caused by E. coli bacteria, HUS may also be caused by certain medications or conditions such as pregnancy, cancer, autoimmune disease or genetic mutations.
HUS is a serious condition. But timely treatment usually leads to a full recovery, especially for young children.
What are the symptoms of E. coli-related HUS?
- Diarrhea, which is often bloody
- Abdominal pain, cramping or bloating
- Vomiting
- Fever
If HUS causes damage to blood vessels, what symptoms indicate that my blood vessels may be damaged?
- Pale coloring, including loss of pink color in cheeks and inside the lower eyelids
- Extreme fatigue
- Shortness of breath
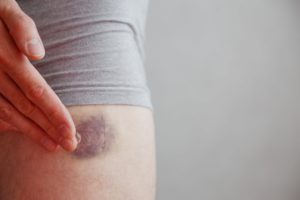
- Easy bruising or unexplained bruises
- Unusual bleeding, such as bleeding from the nose and mouth
- Decreased urination or blood in the urine
- Swelling (edema) of the legs, feet or ankles, and less often in the face, hands, feet or entire body
- Confusion, seizures or stroke
- High blood pressure
When should I see a doctor?
See your doctor immediately if you or your child experiences bloody diarrhea or several days of diarrhea followed by:
- Decreased urine output (oliguria)
- Swelling
- Unexplained bruises
- Unusual bleeding
- Extreme fatigue
- When should I seek emergency care?
- If you or your child have not urinated for 12 hours or more (anuria)
Who is most at risk of developing HUS through E. coli?
- Children 5 years of age or younger
- Adults 65 years of age or older
- People who have a weakened immune system
- People with certain genetic changes that make them more susceptible to HUS
What kind of health problems could develop if I contract HUS?
HUS can cause life-threatening complications, including:
- Kidney failure, which can be sudden (acute) or develop over time (chronic)
- High blood pressure
- Stroke or seizures
- Coma
- Clotting problems, which can lead to bleeding
- Heart problems
- Digestive tract problems with the intestines, gallbladder or pancreas
How can I avoid being infected by E. coli?
Food contaminated with E. coli won’t necessarily smell or taste bad. Below are some tips to help better protect you against the condition.
- Do not eat contaminated meat or produce.
- Avoid unpasteurized milk, juice and cider.
- Wash hands well before eating and after using the restroom and changing diapers.
- Clean utensils and food surfaces often.
- Cook meat to an internal temperature of at least 160 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Defrost meat in the microwave or refrigerator.
- Keep raw foods separate from ready-to-eat foods. Don’t place cooked meat on plates previously contaminated by raw meat.
- Store meat below produce in the refrigerator to reduce the risk of liquids such as blood dripping on produce.
- Avoid unclean swimming areas, especially pools or lakes that are contaminated with feces. Do not swim if you have diarrhea.
Food recalls due to foodborne illness are ubiquitous, and the attorneys at Allen & Allen are experienced in such cases. If you have suffered a foodborne illness through no fault of your own, call Allen & Allen today for a free consultation, at 866-388-1307.